Best price on the market
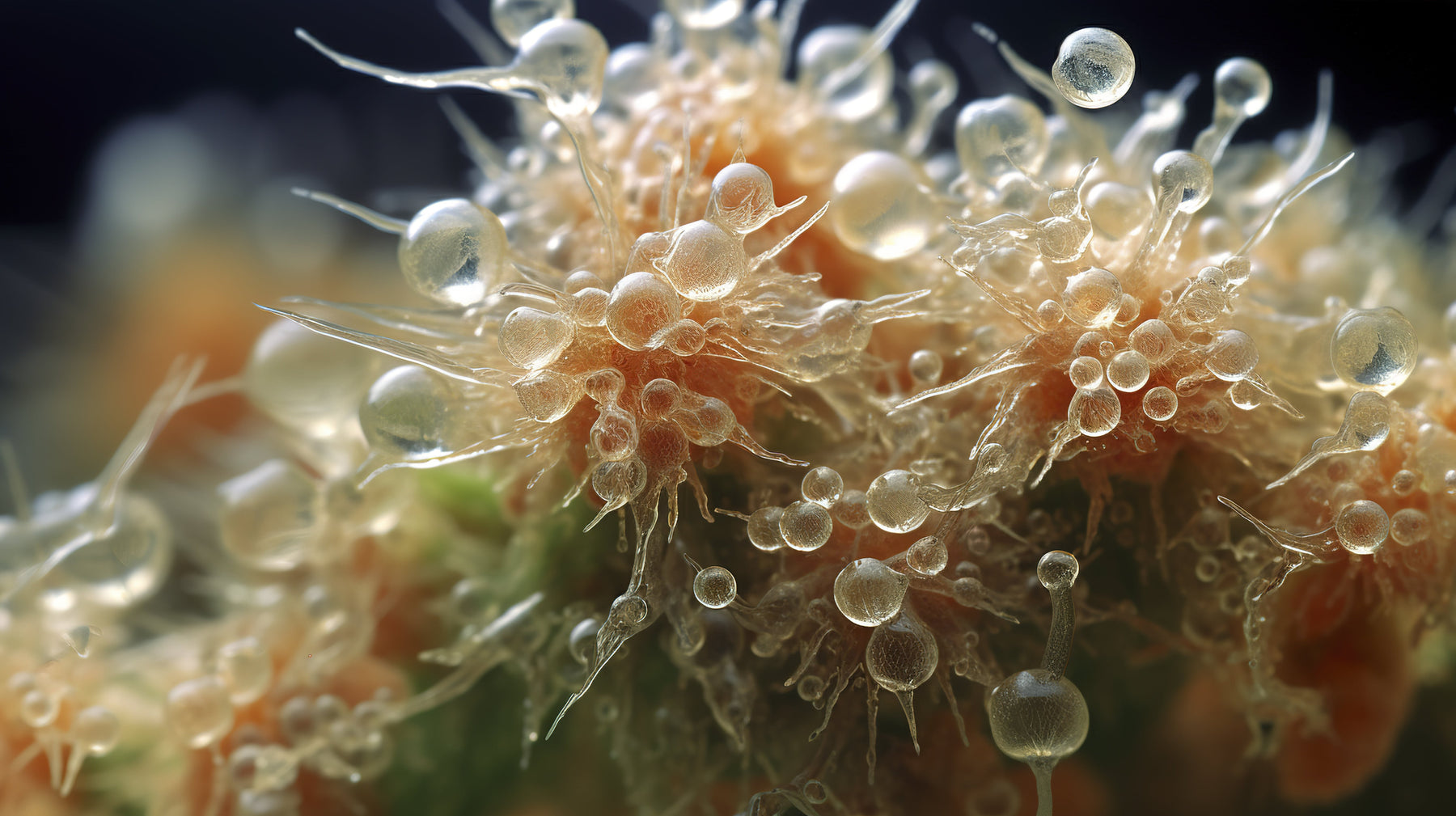
What are Trichomes in marijuana?
Trichomes in marijuana are resinous glands that produce cannabinoids and terpenes, essential for the aroma, flavor and potency of the plant. Visible as crystals, they indicate maturity and quality.
Trichomes, often referred to as the "crystals" or "resin" on the surface of cannabis, are tiny glandular structures that play a crucial role in defining the quality and potency of the plant. To the naked eye, they look like a white or translucent powder, but under a microscope trichomes reveal fascinating complexity. These tiny appendages are responsible for producing and storing cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, and terpenes, which give cannabis its characteristic aromas and flavors.
The importance of trichomes goes beyond their contribution to the psychoactive and therapeutic compounds of cannabis. The state of maturity of Maria Trichomes is a key indicator for growers, indicating the optimal time to harvest. Trichomes ready to harvest indicate that the plant has reached its peak of potency and quality. On the other hand, stale or overripe trichomes can mean a decrease in the quality of the final product. Therefore, detailed observation of trichomes, often with the help of a microscope, is an essential practice in cannabis cultivation.

Anatomy of Trichomes
Cannabis trichomes, tiny but deeply significant structures, have specialized and diverse anatomy. These glandular appendages can be mainly classified into two categories: capitate and non-capitate trichomes.
Capitated Trichomes
These are the most prominent and relevant trichomes for cannabinoid production. They are divided into two main subtypes:
- Capitated Sessile Trichomes : These trichomes have a smaller structure and a glandular head that sits directly on the surface of the plant. Although they produce cannabinoids, their concentration is lower compared to capitate-pedunculated trichomes.
- Capitate Pedunculate Trichomes : These are the largest and most visible, especially under a microscope. These trichomes are made up of a long stem (peduncle) that supports a spherical glandular head. This head is where cannabinoids and terpenes are synthesized and stored. When growers talk about ready-to-harvest trichomes, they are generally referring to the state of these trichomes.
Non-Capitated Trichomes
These are much smaller and less visible. They do not have a distinctive glandular head and their main function is not related to cannabinoid production. Although less prominent, they contribute to the plant's defense against pests and external elements.
In addition to these categories, there are a variety of lesser-known trichomes, each with their own function and structure. However, in the context of cannabis and its desirable properties, capitate-pedunculated trichomes are the most studied and valued, due to their crucial role in the production of precious cannabinoids and terpenes.
The detailed observation of these trichomes, especially their color and structure under the microscope, allows us to determine not only the maturity and the optimal moment for harvesting, but also to predict the cannabinoid and terpene profile of the plant, essential elements to understand the potency. and the effects of cannabis.
Functions of Trichomes
Trichomes on cannabis are not merely microscopic decorations; Its function is vital for the plant and highly valued by growers and consumers. These tiny structures play a central role in the production of the most significant compounds in cannabis: cannabinoids and terpenes.
Cannabinoid Production
Trichomes are the biochemical factories of cannabis, responsible for the synthesis of cannabinoids such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD (cannabidiol), and many others. In the glandular head of the cannabinoid trichomes, especially in the pedunculated capitate trichomes, are the secretory cells that synthesize these compounds from biochemical precursors. THC, known for its psychoactive effects, and CBD, famous for its therapeutic properties, are the most studied and sought after.
The concentration and profile of cannabinoids can vary significantly depending on the maturity of the trichomes. For example, mature trichomes indicate a high concentration of THC, while stale trichomes can signal a degradation of THC into CBN (cannabinol), which has different effects. This is why harvest timing, determined by the state of the cannabinoid trichomes, is crucial to the final cannabinoid profile of the plant.
Terpene Generation
Terpenes are organic compounds that give cannabis its characteristic aromas and flavors. From citrus and fruity to earthy and woody, the diversity of aromas in different cannabis strains is due to the complex mix of terpenes produced in the trichomes. In addition to influencing the sensory experience, terpenes are thought to interact with cannabinoids to modulate their effects, a phenomenon known as the entourage effect.
Terpene production in trichomes is influenced by several factors, including plant genetics, growing environment, and harvest time. Mature trichomes, observable under a trichome microscope, are indicative of a well-developed terpene profile, which translates into a more intense and defined aroma and flavor.

Trichomes and Cannabis Quality
The quality and potency of cannabis are intrinsically linked to the appearance and condition of the trichomes. These tiny structures are not only visual indicators of the maturity and health of the plant, but are also essential in determining the concentration and balance of cannabinoids and terpenes.
Quality and Power Indicators
- Coloration : Maria Trichomes go through a maturation process that is reflected in their color. Initially they are transparent, a sign that the plant is still developing its compounds. As they mature, they become milky or whitish, indicating a higher concentration of THC. Finally, they take on an amber color, suggesting a high level of CBN and a decrease in THC. The proportion of milky and amber trichomes is key to determining the potency and type of effect the cannabis will produce.
- Structure : Trichomes should have a well-formed glandular head and a distinctive stem. Mature and well-developed trichomes are a sign of a healthy and potent plant.
Observation and Analysis Methods
- Use of Microscopes : For accurate evaluation, a trichome microscope is used. These devices allow you to observe the structure and color of the trichomes in detail, which is essential to determine the optimal harvest time and the general quality of the cannabis. Microscopes can range from handheld models to more sophisticated equipment.
- Macro Photography : Macro photography is another technique used to analyze trichomes. Through high-resolution imaging, growers can closely examine trichome maturity and health, even without access to a microscope.
- Visual Inspection : Although less precise, visual inspection with a magnifying glass can provide a general estimate of the condition of the trichomes. However, for large-scale production purposes or to ensure specific quality and potency, the use of more precise tools is recommended.
Harvest and Trichomes
The relationship between the state of the trichomes and the optimal harvest time is one of the most crucial aspects in cannabis cultivation. Close observation of trichomes provides invaluable information on the maturity of the plant and therefore the best time to harvest for maximum potential in terms of potency, effect and flavour.
Relationship between Trichomes and Harvest Time
- Clear or Transparent Trichomes : They indicate that the plant is not yet fully mature. Harvesting at this stage will result in less potent cannabis with fewer psychoactive effects.
- Milky or White Trichomes : This is the point at which the plant has reached its maximum THC concentration. Harvesting at this stage produces cannabis with high potency and pronounced psychoactive effects.
- Amber or Brown Trichomes : The conversion of THC to CBN is most evident in this phase. Harvesting when the majority of the trichomes are in this stage will provide cannabis with more relaxing and sedative effects.
Techniques to identify trichomes ready to harvest
- Microscope Observation : The most precise technique to determine the state of the trichomes is by using a trichome microscope. This allows a detailed evaluation of the color and structure of the trichomes, which is essential for identifying the optimal harvest time.
- Jeweler's Magnifying Glass : A more accessible alternative to the microscope is the jeweler's magnifying glass, which although it does not provide as much precision, can be sufficient for a general estimate of the state of maturity of the trichomes.
- Macro Photography : Macro photography allows growers to document and analyze trichomes in more detail. This technique can be especially useful for tracking the progress of trichome maturation over time.
- Experience and Knowledge : Over time, growers develop an intuitive sense to identify the proper harvest time based on the general appearance of the trichomes and the plant. However, this skill is honed with experience and a deep knowledge of the specific strains of cannabis they are growing.

Extraction and Trichomes
Extraction in the cannabis world refers to the process of separating the cannabinoid- and terpene-rich trichomes from plant matter. Since trichomes are the main sources of the active compounds in cannabis, their role in the production of concentrates and oils is essential. The quality of the final extraction product depends largely on the quality and condition of the trichomes used.
Extraction Methods Focused on Trichomes
- Mechanical Extraction : This method includes techniques such as dry sieving and cold pressing (rosin). Both methods are based on the physical separation of trichomes from plant matter, without the use of solvents. Dry sieving uses screens of different microns to filter out trichomes, while cold pressing applies heat and pressure to extract resinous compounds.
- Solvent Extraction : Methods such as extraction with supercritical CO2, butane (BHO) or ethanol use chemical solvents to dissolve and separate the trichomes from the plant matter. These methods can extract a broader spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes, but require specialized equipment and purification processes to remove solvent residues.
- Extraction with Water and Ice : Known as “water hash” or “bubble hash,” this technique uses cold water and ice to separate the trichomes from the plant. The trichomes become fragile at low temperatures and separate easily, being then filtered through bags with different mesh sizes.
Importance of Trichomes in the Production of Concentrates and Oils
- Concentration of Cannabinoids and Terpenes : Trichomes are the main source of the cannabinoids and terpenes sought in concentrates and oils. A high-quality extraction product requires high-quality, mature trichomes to ensure a rich and potent profile of these compounds.
- Product Diversity : Trichome extraction allows the creation of a variety of products, from shatter, wax, and oils to resins and tinctures. Each extraction method can produce a specific type of concentrate, offering a wide range of textures, potencies, and experiences.
- Purity and Potency : Trichome-focused extraction can produce products with high purity and potency. These concentrates offer a more intense and direct experience of the effects of cannabis, which is especially valuable for therapeutic purposes and for users with high tolerance.
